Content
Phytophthora on tomatoes damages green mass and fruits. Complex measures will help to get rid of this disease. All of them are aimed at destroying harmful microorganisms. By the best means from late blight are considered fungicides. In addition to them, folk methods are widely used.
Signs of the disease
Phytophthora is a fungal disease whose spores persist on seeds, plant debris, greenhouses, and garden tools.
The disease looks like this:
- dark spots appear on the back of the sheet;
- leaves turn brown, dry up and fall off;
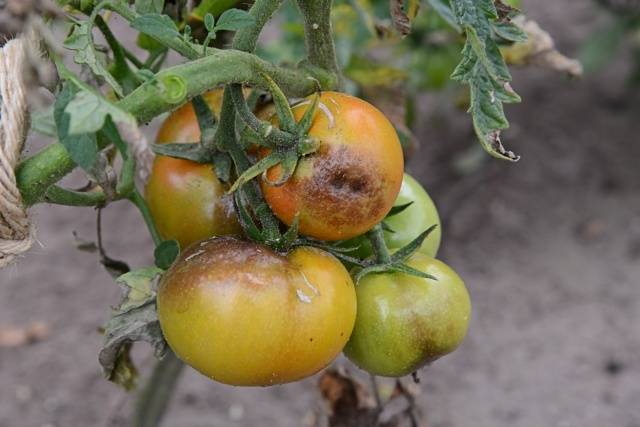
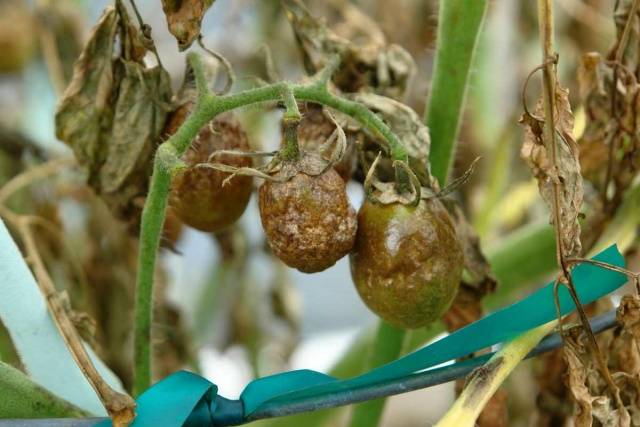
- black bloom spreads on the fruits.
Phytophthora damages the harvest of tomatoes, negatively affects their development. Affected plants should be removed from the area to prevent the spread of the fungus.
In the photo, late blight on tomatoes has spread to the fruits:
Risk factors
Phytophthora begins to develop actively in August, when cold snaps come at night, and fogs appear in the morning. Disease on tomatoes can appear in July, when the temperature drops to 15 degrees and it rains constantly.
The development of late blight occurs under the following conditions:
- too dense planting of tomatoes;
- frequent watering of the soil;
- watering the leaves by sprinkling;
- calcareous soils;
- temperature fluctuations;
- lack of top dressing of tomatoes;
- low temperatures.
Phytophthora spreads from the lower leaves, where moisture accumulates. Therefore, you need to constantly check the planting and, in case of darkening, remove the tomato leaves. Excess foliage and stepchildren must be removed, as well as yellowed and dried leaves.
Drug treatment
To get rid of late blight, special preparations are used that contain copper. The fungus of the disease is able to adapt to different conditions, so it is best to combine several methods. If late blight appears on tomatoes, treatment is started immediately to prevent the spread of fungal spores.
Use of fungicides
For processing plantings tomatoes from late blight the following preparations with fungicidal properties are used:
- Fitosporin - a natural preparation containing beneficial bacteria, one of the most effective according to gardeners' reviews. When interacting with soil and plants, Fitosporin destroys harmful spores of diseases. The drug heals the affected tissues, strengthens the immunity of tomatoes and accelerates their growth. 200 g Fitosporin requires 0.4 liters of warm water. The solution is used for treating seeds, soil or spraying tomatoes.
- Fundazol - a systemic drug capable of penetrating plants and providing a disinfectant effect. Treatment is carried out by watering the soil, spraying tomatoes during the growing season, and seed dressing. 1 g of Fundazole is diluted in 1 liter of water. The tool is used twice throughout the season. The last treatment is carried out 10 days before the fruit is removed from the bush.
- Quadris - a systemic fungicide that penetrates into plant tissues and allows you to fight late blight on tomatoes. The remedy is effective in the early stages of the disease, when the first signs of phytophthora appear. Quadris is not dangerous for humans and plants. It can be applied 5 days before picking tomatoes. The number of treatments per season is no more than three.
- Horus - a drug with a protective and therapeutic effect, which effectively fights late blight. The tool works at any time of the year, however, its properties decrease when the temperature rises to 25 degrees. Therefore, Horus is used to prevent late blight in early spring. The therapeutic effect of the drug lasts 36 hours.
- Ridomil - a drug consisting of two components: mefenoxam and mancoceb. Mefenoxam has a systemic effect and penetrates into plant tissues. Mancozeb is responsible for the external protection of tomatoes. To combat late blight, a solution is prepared consisting of 10 g of the substance and 4 liters of water. Ridomil is used by leaf processing of tomatoes. The first procedure is performed before the onset of the disease. After 10 days, the treatment is repeated. The next spraying is carried out 2 weeks before the fruit is removed.
- Previkur - a fungicide with a wide range of effects. The drug stimulates the growth of tomatoes, strengthens the immune properties, and allows you to treat tomatoes. For 1 liter of water, 1.5 ml of Previkur is enough. Processing is carried out in dry weather at a temperature of 12-24 degrees by watering or spraying. The action of the components begins in 3-4 hours. Previkur shows its properties within three weeks.
- Trichopolus - an antibiotic used to combat late blight on tomatoes. Trichopolum tablets (10 pcs.) Are diluted in 5 liters of warm water. The solution is used for spraying tomatoes. Up to three treatments with the drug can be carried out per month. The use of the product is discontinued during the ripening of the fruit.
Bordeaux liquid
Another way to get rid of late blight on tomatoes is Bordeaux liquid. This product is prepared on the basis of copper sulfate, which looks like microscopic blue crystals. A solution of this substance has a high acidity, therefore, Bordeaux liquid is prepared on its basis.
At an early stage of tomato development and after harvesting, a 3% solution per 10 liters of water is used:
- 0.3 kg vitriol;
- 0.4 kg of lime.
Preliminarily, two solutions are prepared from these components. Then the vitriol solution is carefully poured into milk of lime. The resulting mixture should stand for 3-4 hours.
Be sure to use protective equipment for hands and respiratory organs. It is not allowed to get the solution on the mucous membranes and skin.
Processing is done by spraying tomato leaves. The solution should completely cover the sheet plate.
Copper oxychloride
Substitute bordeaux liquid is oxychloride copper... This fungicide has a protective contact effect and allows you to solve the problem of how to deal with late blight. For spraying, a solution is prepared by mixing the drug with water.
The treatment of tomatoes with copper chloride is carried out in several stages. The first treatment is performed when the first symptoms of the disease are detected. Then the treatment is repeated after 10 days. In total, no more than 4 procedures are allowed.
The last treatment is done 20 days before harvest. The rate of the drug must be strictly observed in order to prevent the formation of leaf burns.
Various preparations have been developed on the basis of copper oxychloride: Hom, Zoltosan, Blitoks, Cupritoks. For every 10 square meters, 1 liter of the final solution is required. The fight against late blight on tomatoes by this method is carried out during the growing season of plants.
Folk remedies
Folk recipes are used in addition to the main methods of treatment. They are used as a prophylaxis for disease when it is necessary to disinfect soil and plants.
Iodine solution
Iodine-based solution helps at the first signs of phytophthora. The first treatment is performed in mid-June, then it is repeated a week later. The final procedure is performed in July.
The solution can be prepared using water (10 L) and iodine solution (5 ml).Spraying is carried out in the absence of direct exposure to the sun, in the morning or in the evening.
With iodine deficiency, fruits are tied and ripen more slowly, the immunity of tomatoes decreases, thin stems are formed, and the foliage becomes pale and lethargic.
Before flowering, iodine solution is used for watering the soil. To do this, add three drops of iodine to 10 liters of warm water. One bush requires 1 liter of solution.
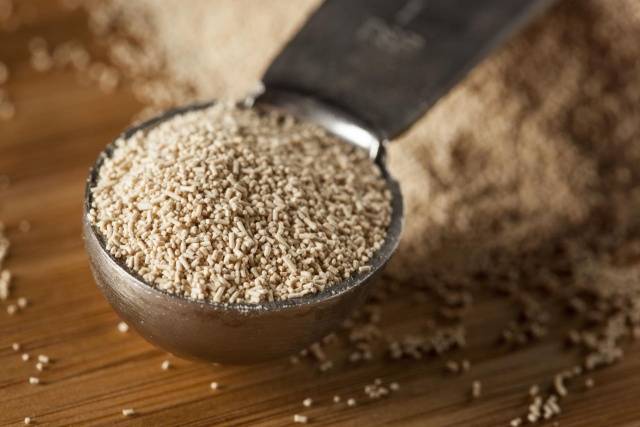
Yeast feeding
One of the methods of how to deal with late blight on tomatoes is the use of yeast feeding.
Yeast contains fungi that can displace harmful microorganisms from plants and soil. After yeast treatment, the growth of vegetative mass is accelerated, the endurance of seedlings increases, and the resistance of tomatoes to external factors increases.
You can use yeast a week after planting tomatoes in a permanent place. To prepare the solution, you will need the following components:
- dry yeast - 10 g;
- extract from chicken droppings - 0.5 l;
- ash - 0.5 kg;
- sugar - 5 tbsp. l.
The resulting mixture is diluted in 10 liters of water and applied by irrigation under the root of tomatoes. The procedure is carried out for the prevention of late blight every 10 days.
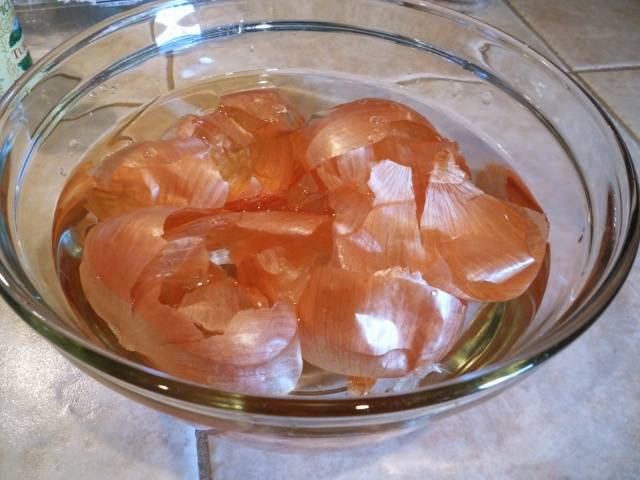
Garlic or onion infusion
The main step in deciding how to save tomatoes from late blight is soil disinfection and plants.
Garlic and onions contain phytoncides that can fight harmful spores. Watering with an infusion based on onions or garlic improves the structure of the soil and saturates it with useful substances.
To prepare the product, the heads, arrows or husks of these plants are used. 2 cups of onions or garlic are poured with 2 liters of boiling water. The infusion is prepared within 48 hours. The resulting liquid is diluted in a 1: 3 ratio.
The second yeast feeding is done during the flowering period. Tomatoes are watered at the root in the evening. For the prevention of late blight, plant leaves are sprayed with a solution.
Milk serum
Whey contains beneficial bacteria that can suppress phytophthora spores. After processing with whey, a thin film forms on the leaf plate, which serves as a protection against the penetration of harmful microbes.
The disadvantage of this method is its short duration. When precipitation falls, the protective layer is washed off. 1 liter of whey is mixed with 9 liters of water at room temperature. Tomatoes are processed in May-June.
Saline solution
For the prevention of phytophthora, a saline solution works effectively. It is obtained by dissolving 1 cup of table salt in a bucket of water.
Due to the salt, a film is created on the surface of the leaves that protects the plants from the penetration of fungus. Therefore, the solution is used by spraying plants.
Salt infusion is applied during the formation of ovaries. When the first symptoms of the disease appear, you first need to remove the affected parts from the tomato, and then carry out the treatment.
Prevention measures
The following measures will help save tomatoes from late blight:
- plant onions or garlic between rows of tomatoes (every 30 cm) or in adjacent beds;
- in the greenhouse, you can plant mustard, which has disinfectant properties;
- selection of varieties resistant to late blight (Dragonfly, Blizzard, Casper, Pink Dwarf, etc.);
- plant early ripening tomatoes to harvest before the spread of the disease;
- observe crop rotation (plant tomatoes after cucumbers, onions, legumes, greens, zucchini, carrots);
- do not plant in a garden where potatoes, peppers or eggplant previously grew;
- avoid high humidity in the greenhouse or greenhouse;
- disinfect the soil before planting tomatoes;
- fertilize regularly;
- observe the distance between landings;
- make moderate watering;
- process the greenhouse in the spring with Fitosporin solution.
Conclusion
The fight against late blight is complex. To protect tomatoes, the rules for planting, watering and feeding are observed. When signs of a disease appear, treatment with special preparations is performed. Additionally, you can use folk remedies that have their own benefits.