Content
Red currants, like black and white varieties, are among the most popular berry bushes grown in Russia. Caring for her is quite simple and usually does not present difficulties for the gardener, for this she is loved and appreciated. On a personal plot, you can plant red currants in spring, as well as in autumn, this is very convenient, first of all, for those who have difficulties with planting material.
Features of growing red currants
Unlike their black variety, red currants are not as popular. This is largely due to the nuances of using the crop. The fruits of black currant are distinguished by a more pronounced taste, its berries contain much more vitamins and microelements. The leaves of this shrub are used for home canning. Red currant is seriously limited in use, its berries have a less intense and more watery taste, and the content of vitamins and nutrients in them is slightly lower.
Despite this, red currants are grown mainly for fresh consumption, compotes or jam. The vegetation of this shrub begins quite early in spring, immediately after the average daily temperature rises above 0 ° C. For a year, currants give a fairly strong increase, especially at a young age. The basal shoots also grow abundantly, from which you need to partially get rid of, leaving only 2-3 of the most powerful shoots annually, evenly growing around the circumference of the bush.
Red currants bear fruit for quite a long time. Unlike black, which yields mostly on shoots for 2-3 years of life, red can give a good yield on 7-8 year old branches. Therefore, these bushes live longer, they need less pruning, the shoots do not grow very much in breadth, stretching more upward. Red currants bear fruit along the entire length of the shoot, while in the black, the main crop grows in the lower part.
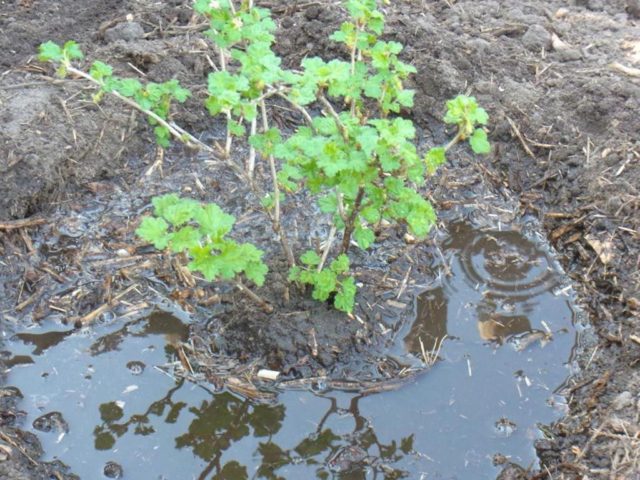
There are few differences in care between these berry bushes. All varieties of currants prefer the same growing conditions, they require a well-lit area and loose, well-drained soil on the site. Watering is needed regularly, but very moderate, it is impossible to overmoisten the soil. Currant reacts very painfully to excess water in the roots and may die. However, drought is unacceptable for her. It is advisable to feed the bushes several times a year, especially if the soil is poor. The root zone must be cleared of weeds and mulched. For the winter, currant bushes are not covered, it is enough just to cover them with snow.
How to plant red currants in spring: step by step instructions
Spring is not the optimal time for planting berry bushes, including red currants. A more favorable time for this is autumn, since at this time of the year there are no problems with seedlings, the time interval for work is quite wide and you do not need to do everything in the literal sense of the word running.However, planting in autumn may not be possible in regions with early winter, since the planted seedlings may not have time to take root before the onset of frost, so they are guaranteed to die in winter or next spring.
When is it better to plant red currants
To plant a red currant seedling in open ground in the spring, you need to choose a time when the buds of the seedling have not yet blossomed, but the ground has already thawed. In different regions of the country, this time falls in April or early May. If leaves appear on the seedlings, then rooting will be worse. With warming weather, the survival rate of young bushes decreases, especially in seedlings with an open root system, and planting at this time without a root stimulator in most cases ends in failure.
Where is the best place to plant red currants
Often, gardeners plant red currants according to the leftover principle, allocating a place for it near the fence somewhere in the backyard of the garden. With this approach, there is no need to wait for a good harvest. For planting red currants, you must select an open, sunny place, preferably without cold wind and drafts. You should not plant it too close to buildings or structures, the optimal distance is 1.5-2 m. Red currants will grow well even if you plant it next to low trees with a loose crown that allows diffused sunlight to pass through.
The soil for currants should be loose, breathable and moderately moist. Fertile soils with neutral acidity are well suited for this crop. Water should not linger in the soil, its excess causes diseases in currants. Therefore, low-lying, swampy and wetlands for planting this shrub cannot be chosen. Groundwater should lie at a depth of at least 1 m. If this indicator is less than the recommended one, then an artificial embankment should be made before planting the shrub.
Many garden crops are suitable as precursor plants for red currants:
- vegetables;
- greens;
- siderates;
- legumes;
- cereals;
- flowers.
You can not plant red currants after gooseberries or raspberries, these shrubs have common enemies - pests and suffer from similar diseases.
How to prepare a landing site
The site for planting red currants in the spring must be prepared in the fall. The place must be cleared of weeds, debris, stones. The top layer of the soil must be dug up, at the same time organic fertilizer must be applied. Humus is best suited for this purpose; 1-2 buckets per 1 sq. m. It is advisable to add wood ash to the soil in the amount of 0.5-1 kg for the same area. Additionally, you can use mineral fertilizers (superphosphate, potassium sulfate), but they can be applied in the spring, with the direct planting of seedlings.
How to plant red currants
The size of the planting pit for a red currant seedling must be guaranteed to be larger than the volume of its roots. As a rule, a hole with a diameter of 0.5-0.6 m and the same depth is sufficient. It is advisable to dig holes in advance so that the soil has time to settle and be saturated with air. The soil taken out of the pit is mixed with mineral fertilizers and ash, if these components were not introduced in the fall when digging the site. A little of this mixture is poured into the bottom of the pit, and then 1-2 buckets of water are poured into it and allowed to soak.
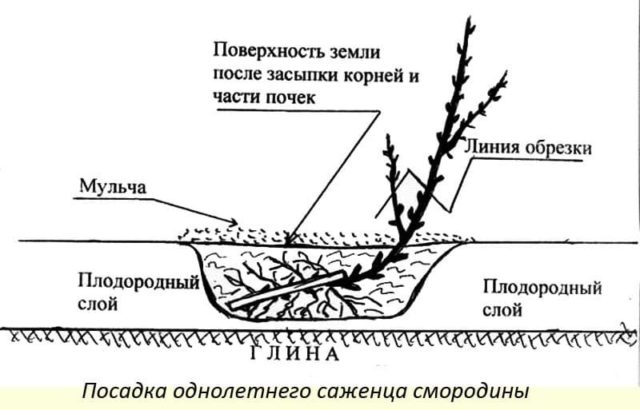
The planting procedure itself is the same in spring and autumn. The seedling must be installed in the planting hole at an angle of approximately 45 °, spread its roots and fill it with prepared soil, periodically compacting it. At the same time, the root collar is deepened by 5-8 cm, which ensures the rapid growth of new shoots and the accelerated formation of a strong fruiting bush. After the hole is completely filled up, a small circular ditch 8-10 cm deep is made around the seedling, which is completely filled with water.Instead, build an earthen roller of the same height around the bush to keep the water from spreading. After watering, the root zone is mulched with peat or humus to avoid evaporation of moisture from the soil.
What to plant next to red currants
A white variety is usually planted next to red currants, while varieties of different ripening periods can be used, this will extend the harvest time. Often, for the convenience of work, gooseberries are placed near these bushes; these plants have similar agricultural techniques. But black currants next to red ones will grow worse, such a neighborhood oppresses both. It is not recommended to plant red currants next to bush cherries or other trees that form numerous root shoots, this can additionally thicken the bush and make it difficult to work with it.
To protect against insect pests, onions or garlic are often planted next to this shrub, the pungent smell of these plants scares off aphids and currant mites.
How to properly care for red currants
Red currant is a rather unpretentious plant, however, in order for it to feel good and bear fruit abundantly, it is necessary to carry out a number of mandatory measures. These include:
- watering;
- top dressing;
- pruning;
- loosening and mulching of the root zone.
Watering and feeding
Despite the fact that red currant belongs to moisture-loving crops, it needs very moderate watering, albeit regular. Its root system is quite branched and powerful, which makes it more resistant to drought than the black variety. However, the lack of moisture has a detrimental effect on the shrub. The shoots, which are already characterized by a small annual growth, begin to lag far behind, and the berries become smaller and crumble, without having time to fill up.
To avoid this, during the period of setting and ripening of berries, red currant bushes should be watered regularly, especially if the summer is dry. The rate of water consumption at this time is 3-4 buckets per 1 bush, the frequency of watering is 1 time in 6-10 days. In order for moisture to be better retained in the soil, a groove is often built around the bush with a depth of 8-10 cm inside the projection of the crown. During watering, it is filled with water, and then covered with a dense material, for example, a piece of roofing material. Mulching the root zone with peat, humus or straw will help to keep moisture in the soil longer.
Caring for red currants necessarily includes fertilizing. For feeding shrubs in early spring, urea is most often used. It is enough to add 20-30 g for each bush, scattering the granules in the root zone. At the beginning of summer, it is advisable to use organic fertilizers for feeding, for example, slurry or infusion of chicken droppings. Instead of organic matter, urea and superphosphate can be used.
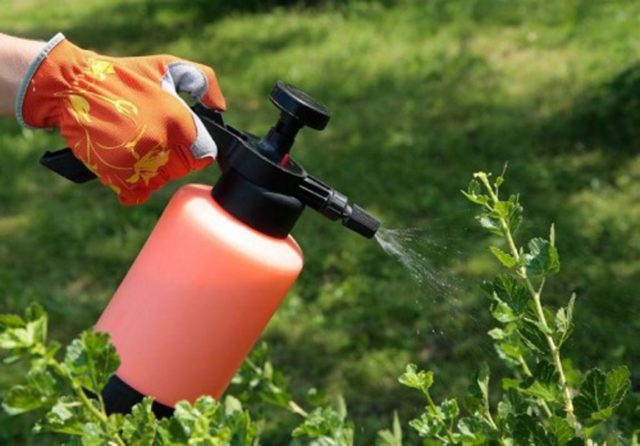
During the period of filling and ripening of berries, red currants need microelements. It is better to do such a top dressing by foliar method. This will require:
- Boric acid - 2.5 g.
- Manganese sulfate - 5 g.
- Copper sulfate - 1 g.
- Ammonium molybdate - 2 g.
- Zinc sulfate - 2 g.
All components dissolve in 10 liters of water. This composition is used for processing shrubs. This should be done in the evening so that the solution has time to be absorbed before the water evaporates from the surface of the leaves.
The last time in the season, red currant bushes are fed in late autumn. At this time, the aisles are dug up with the simultaneous introduction of rotted manure, and superphosphate (50-100 g per bush) is added under the bushes.
Pruning
Pruning of red currant bushes is done annually, in early spring or autumn. During the procedure, diseased, broken, excess shoots, as well as thickening root shoots are removed. Old shoots begin to be removed after 7-8 years, thus, the bush gradually rejuvenates.Unlike black currants, red ones do not undercut annual growth, since most of the crop ripens on it.
Protection against diseases and pests
With proper agricultural technology, red currants are relatively rare. However, in case of violations in care, especially associated with excessive watering, powdery mildew or other fungal diseases may appear on the bushes. They fight them by treating the bushes with various fungicides. Red currants are also affected by viral diseases such as mosaic and terry. Most often, their carriers are insect pests, such as aphids, weevils, kidney and spider mites, etc., various chemical and biological preparations are used to destroy them.
Preparing for winter
Red currants are resistant to low temperatures and require no shelter for the winter. It is enough just to cover the bushes with snow. Before winter, a layer of mulch is removed from the root zone of the shrub, and the soil is dug up. This measure contributes to the fact that most of the insect pests wintering in the upper layer of the earth simply freeze out.
Tips from seasoned gardeners about caring for red currants in spring
Many gardeners recommend adhering to the following rules when growing and caring for red currants.
- It is imperative to process the bushes with hot water in early spring. This can be done with a regular watering can. Sprinkling with boiling water kills currant mites, as well as fungal spores.
- Red currant bushes, in contrast to black, grow stronger upward than in breadth. Therefore, when planting them, the intervals between adjacent bushes can be made smaller.
- To prevent the bush from falling apart, it is advisable to install a fence around it.
- Do not rush to cut out old shoots. In red currants, with good care, they can bear fruit for up to 15 years.
- The mulch layer should not touch the currant shoots. Otherwise, in the places of contact, the bark may crack, which is fraught with infections.
- If the bush is sick with mosaic or terry, it is better to remove it entirely and be sure to burn it. These viral diseases are not cured, if you delay, you can lose the neighboring plantings.
For more information on planting red currants in spring, see the video
Conclusion
It is possible to plant red currants in spring in many regions, and for areas with an early arrival of winter, this method is uncontested. The planting process itself is quite simple and usually does not cause difficulties even for beginners, the most important thing for spring planting is meeting the deadlines. If you choose the right time and place for planting, then the shrub will take root perfectly and will delight you with excellent yield for a long time.